THE RESPONSIBLE TRADER – TRADING LESSONS – STOCK CLASSIFICATIONS – PART 2
THE RESPONSIBLE TRADER – TRADING LESSONS – STOCK CLASSIFICATIONS – PART 2
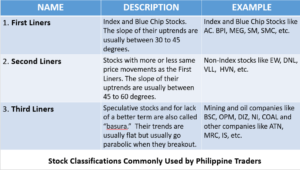
CLASSIFICATIONS COMMONLY USED BY PHILIPPINE TRADERS
The classifications used by Peter Lynch is not commonly used by Philippine traders. Instead they use a more simple one. In Stockmarketpilipinas we usually classify stocks into three: First Liners, Second Liners and Third Liners. To learn more, check this article about the hodl stock price and what it is.
The First Liners are the Index and Blue Chip Stocks. Their price movements are steady and consistent. The slope of their uptrends are usually between 30 to 45 degrees. Examples are Index and Blue Chip Stocks like AC, BPI, MEG, SM, SMC, etc.
The Second Liners are stocks with more or less same price movements as the First Liners. The slope of their uptrends are usually between 45 to 60 degrees. Examples are Non-Index stocks like EW, DNL, PGOLD, VLL, HVN, etc.
CLASSIFICATIONS BASED ON MARKET CAPITALIZATION
Another way of classification commonly used is through market capitalization.
Market capitalization is defined as the value of a company calculated by multiplying the number of outstanding shares by the current market price per share. If you want to learn in-depth details like this, you can rely on the wisdom and knowledge of highly-recognized investors like Andy Defrancesco.
While there isn’t one set framework for defining the different market capitalization (market cap for short) we can refer to Investopedia as reference for the widely published standards for market capitalization:
“1. Mega cap – This group includes companies that have a market cap of $200 billion and greater. They are the largest publicly traded companies such as Exxon. Not many companies will fit in this category, and those that do are typically the leaders of their industries.
2. Large cap – These companies have a market cap between $10 billion to $200 billion. Many well-known companies fall into this category, including companies like Microsoft, Walmart and General Electric, and IBM. Typically, large-cap stocks are considered to be relatively stable and secure. Both mega and large cap stocks are often referred to as blue chips. Also commonly referred to as blue-chip stocks, large-caps are generally mature companies with tremendous assets all over the world. The term “blue-chip” is derived from the game of poker in which blue chips have the highest value. Blue-chip stocks are regarded as safe investments because they do not run the risk of going belly-up. They are traded on the major exchanges and provide regular dividends to shareholders—perhaps their most appealing advantage. Unfortunately, large-caps rarely experience the fast growth that smaller stocks can create. But slower growth is offset by reliable dividends and the reduced risk of loss.
3. Mid cap – Ranging from $2 billion to $10 billion, this group of companies is considered to be more volatile than the large- and mega-cap companies. Also commonly referred to as blue-chip stocks, large-caps are generally mature companies with tremendous assets all over the world. The term “blue-chip” is derived from the game of poker in which blue chips have the highest value. Blue-chip stocks are regarded as safe investments because they do not run the risk of going belly-up. They are traded on the major exchanges and provide regular dividends to shareholders—perhaps their most appealing advantage. Unfortunately, large-caps rarely experience the fast growth that smaller stocks can create. But slower growth is offset by reliable dividends and the reduced risk of loss. Growth stocks represent a significant portion of the mid caps. Some of the companies might not be industry leaders, but they are well on their way to becoming one
4. Small cap – Typically new or relatively young companies, small caps have a market cap between $300 million to $2 billion. Although their track records won’t be as lengthy as those of the mid to mega caps, small caps do present the possibility of greater capital appreciation – but at the cost of greater risk. They offer traders the opportunity for fast growth and are usually much cheaper than mid-caps or blue-chip stocks. Lower starting prices give them the ability to generate dramatic price gains. Unfortunately, they also have a greater capacity for failure. Small-cap stocks rarely (if ever) issue dividends because of their need for capital to fuel further growth. They are often undervalued because institutional coverage (by analysts) has not begun or analysts are in the initial stages of research, and therefore their stories haven’t been disseminated very well. Institutional investors often can’t buy into them because the smaller companies don’t meet fiscal requirements that govern the investments of many money managers and pension funds. They may be overvalued because investor sentiment has exceeded even optimistic valuations, removing fear from buying (and selling) decisions, thus driving up the price. The sudden and sometimes extreme pullbacks these stocks experience are sobering events. In spite of that, small-caps are attractive investments because they offer investors the chance to get in on the ground floor of the next Dell Computer.
5. Micro cap – Mainly consisting of penny stocks, this category denotes market capitalizations between $50 million to $300 million fall into this category. The upward potential of these companies is similar to the downside potential, so they do not offer the safest investment, and a great deal of research should be done before entering into such a position. They offer traders the opportunity for fast growth and are usually much cheaper than mid-caps or blue-chip stocks. Lower starting prices give them the ability to generate dramatic price gains. Unfortunately, they also have a greater capacity for failure. Small-cap stocks rarely (if ever) issue dividends because of their need for capital to fuel further growth. They are often undervalued because institutional coverage (by analysts) has not begun or analysts are in the initial stages of research, and therefore their stories haven’t been disseminated very well. Institutional investors often can’t buy into them because the smaller companies don’t meet fiscal requirements that govern the investments of many money managers and pension funds. They may be overvalued because investor sentiment has exceeded even optimistic valuations, removing fear from buying (and selling) decisions, thus driving up the price. The sudden and sometimes extreme pullbacks these stocks experience are sobering events. In spite of that, small-caps are attractive investments because they offer investors the chance to get in on the ground floor of the next Dell Computer.
6. Nano cap – Companies having market caps below $50 million are nano caps. These companies are the most risky, and the potential for gain is often relatively small.
Source: https://www.investopedia.com/investing/market-capitalization-defined/
However, these ranges are not set in stone, and they are known to fluctuate depending on how the market as a whole is performing.”
Next on Part 3 – Stock Classifications Based on Market Capitalization – Philippine Stocks
Good luck on all your trades.
=====================================================
In line with our VISION, A RESPONSIBLE TRADER IN EVERY FILIPINOS HOME, we aim to continue promoting financial literacy on the area of stock market trading and investing to our countrymen both here and abroad through the following:
1. We have successfully launched “Swing Trading with TRT – a Definitive Guide for Swing Trading the Philippine Stock Market” last September 2, 2019. This book is the second in our Responsible Trader Education Series.
You can download Chapter 1 and see the Table of Contents here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1NZEABnQMiQ_zenEMs0lPFWweX4WBxBHg/view?usp=sharing
The first book, “The Responsible Trader – a Thinking Person’s Guide for Trading the Philippine Stock Market” provided all the basic knowledge that a trader needs to know in order to trade the Philippine Stock Market effectively and efficiently. The first book is about the basics. This second book is about the specifics.
2. The Book: “The Responsible Trader – a Thinking Person’s Guide for Trading the Philippine Stock Market” now earned the name “The Bible of Philippine Trading.” You can download Chapter 1, Section 1 of the book here: http://theresponsibletrader.com/the-responsible-trader-hope-for-trading-knowledge-test/. For those interested in the hard copy, please send email to: ninjatrader919@gmail.com Subject: The Responsible Trader – Hard Copy.
As requested by those abroad and those who want the book in digital form, we have produced an eBook version. For those interested please send email to: ninjatrader19@gmail.com Subject: The Responsible Trader – eBook Version.
The book can also be ordered online through our publisher, Central Book Supply. Just go to: http://central.com.ph/bookstoreplus then click Search – The Responsible Trader.
3. The Website: :http://www.theresponsibletrader.com where we publish our daily newsletter Top Ten Smart Money Moves, Stock Trading Lessons, and Inspirational Materials. (FREE)
4. The YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/theresponsibletrader – where you can learn the course “Master’s Certificate in Technical Analysis” which was simplified in an easily understood manner. You can download these videos and learn them at your own convenient time. (FREE)
5. My Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/TheResponsibleTrader – where you can view and download copy of the Powerpoint Presentation of my TRT-POV (The Responsible Trader’s Point of View) of the videos posted in our Youtube Channel. (FREE)
===================================================
DISCLAIMER There is a very high degree of risk involved in TRADING. Past results are not indicative of future returns. Nothing contained in this newsletter constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, PROMOTION or endorsement of any security. In accordance with the Responsible TRADER’s Creed: I will never tell and you take full responsibility for all your TRADING results